| Copyright © Klaus Piontzik | ||
| German Version |
| The galaxies that accompany our Milky Way can also be arranged concentrically around our galaxy. |
.
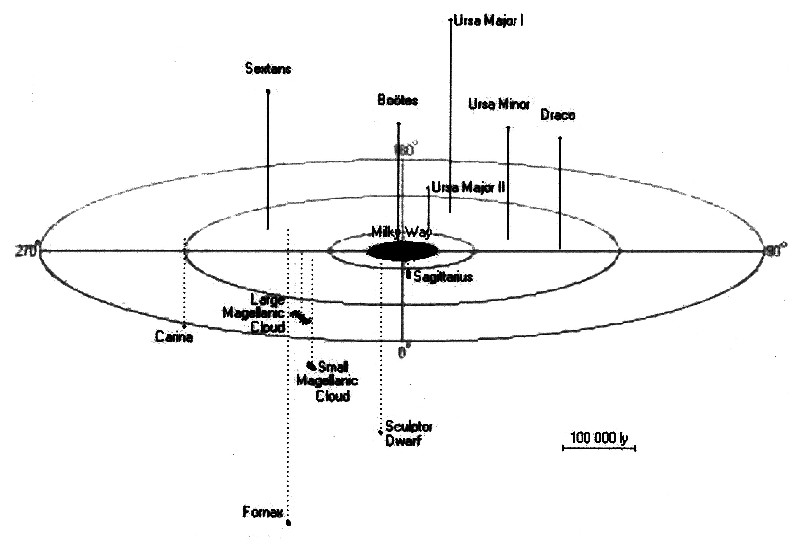
Illustration 8.5.1 – Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way
|
The table below contains all the objects commonly seen as satellite galaxies.
As can be seen from the tolerances in the table, the distances are sometimes subject to major inaccuracies. The distances are given in light years. The light year [Ly] is an astronomical unit of measurement. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. 1 light year [Ly] = 9.461 trillion Km = 9.461·10 12Km The logarithmic values ??of the distances are again plotted as a function of the numbering, which is shown in Figure 8.5.2. As can be seen, there is already good linearity in most of the values. |
| Galaxy | Nr | Distance | Tolerance | ln(Distance) |
| kiloLy | kiloLy | |||
Canis major dwarf |
0 |
24 |
3,17805383 |
|
Sagittarius dwarf elliptical galaxy |
1 |
78 |
±7 |
4,35670883 |
Ursa-Major-II |
2 |
100 |
±15 |
4,60517019 |
Complex H |
3 |
108 |
4,68213123 |
|
Bootes II dwarf |
4 |
136 |
±26 |
4,91265489 |
Willman 1 |
5 |
147 |
4,99043259 |
|
Bootes III dwarf |
6 |
150 |
5,01063529 |
|
Large Magellanic Cloud |
7 |
165 |
±5 |
5,10594547 |
Small Magellanic Cloud |
8 |
195 |
±15 |
5,27299956 |
Bootes-I-Dwarf |
9 |
196 |
±9 |
5,27811466 |
Ursa Minor Dwarf |
10 |
215 |
±10 |
5,37063803 |
Sculptor dwarf |
11 |
258 |
±13 |
5,55295958 |
Draco dwarf |
12 |
267 |
±20 |
5,58724866 |
Sextans dwarf |
13 |
280 |
±13 |
5,6347896 |
Ursa Major I |
14 |
325 |
5,78382518 |
|
Carina dwarf |
15 |
329 |
±16 |
5,79605775 |
Hercules dwarf |
16 |
430 |
6,06378521 |
|
Fornax dwarf |
17 |
450 |
±26 |
6,10924758 |
Canes-Venatici-II |
18 |
490 |
±49 |
6,19440539 |
Leo II |
19 |
669 |
±39 |
6,50578406 |
Canes-Venatici-I |
20 |
718 |
±82 |
6,57646957 |
Leo I |
21 |
815 |
±82 |
6,70318811 |
Phoenix dwarf |
22 |
1450 |
±100 |
7,27931884 |
Barnard's Galaxy |
23 |
1600 |
7,37775891 |
|
Leo III |
24 |
2250 |
±325 |
7,7186855 |
Tucana dwarf |
25 |
2870 |
±130 |
7,96206731 |
|
The e-function can be determined again from the linearized values.
The equation for the approximation line is:
y = ln R = 0.1382·x + 3.178 The following applies to the distances: R = 24·e0.1382x[kiloLy] The logarithmic distances of the galaxies are shown in Figure 8.5.2. The complete e-function for the galaxies can be seen in Figure 8.5.4. |
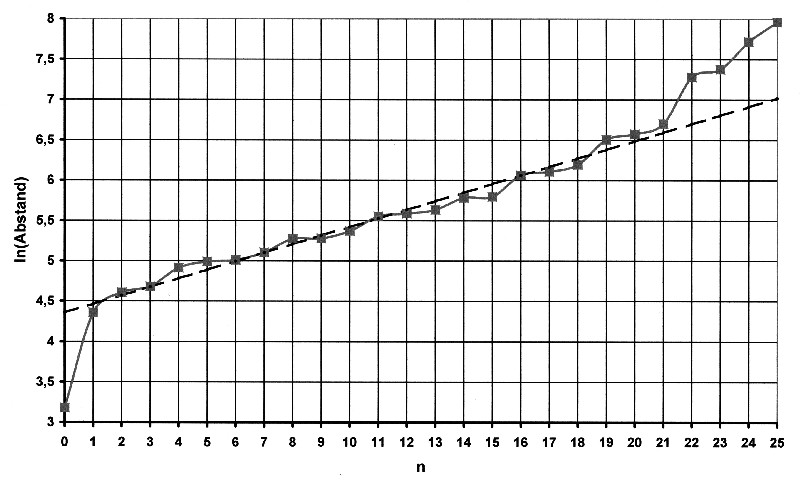
Illustration 8.5.2 – Logarithmic galaxy distances
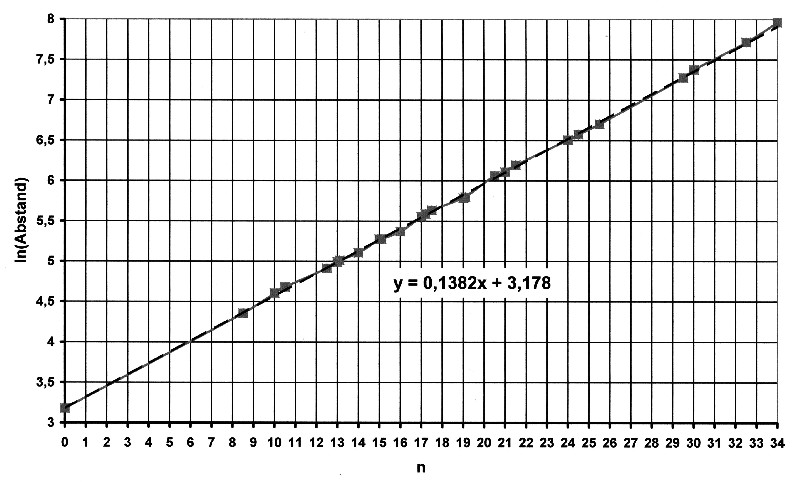
Illustration 8.5.3 – Linearization

Illustration 8.5.4 – Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way

|
200 sides, 23 of them in color 154 pictures 38 tables Production und Publishing: ISBN 978-3-7357-3854-7 Price: 25 Euro |